What is ERP and why do so many companies have it?
Centralized enterprise resource planning and management
An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), or enterprise resource planning system, is a software that allows companies to control all the information flows generated in each area of the organization.
This software is one of the most requested tools by companies, regardless of their size or area of activity, to be able to coordinate from a single tool several or all their departments and thus optimize the resources of their organization to the maximum.
More than a tool, an ERP is a way for a company to centralize all the necessary functions to manage its business in the most efficient way possible.
What are the objectives of an ERP?
One of the main objectives of ERP systems is to unite or integrate the different departments into a single tool. Previously, each department had its own specialized program. Thanks to these ERP systems, now, from the same centralized database, all the company’s information is managed live and more efficiently.
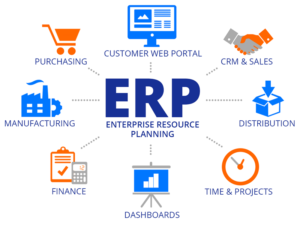
Therefore, coming from this integration, ERP systems usually have different modules within the tool, each one corresponding to each department of the organization. Depending on the type of company these modules may vary, but the most common ones are usually purchasing, sales, inventory, invoicing, logistics, accounting, HR and CRM.
The ultimate goal, and why this tool is so sought after, is to help companies in administration and decision making, through the automation of their processes. As a result, fewer errors are made, less time is wasted and, therefore, the profitability of an organization is improved.
Another reason why this type of software is so successful may be that enterprise resource planning is often tedious or difficult to carry out. With an ERP system, however, this process is automated.
Types of ERP
Having defined and explained their purpose, in order to understand ERP systems, it is important to know what types there are and their categorization according to two fundamental factors: the size of the organization and the location of the ERP.
According to the size of the organization
This categorization responds to the different variations that, depending on the size of the company, may require some features or others within the ERP system.
– ERP for small businesses
Designed and focused for local businesses, this ERP can change its features according to the complexity that these small companies may present. They can also be very useful for managing the information of organizations that operate in a very specialized sector.
- ERP for SMEs
The characteristic of these ERPs that varies from the previous ones is scalability, since they are designed to grow along with the companies. These ERPs are designed to cover the business processes of more than one industry.
- ERP for large companies
These ERPs are the most powerful on the market as they are designed to support the complexity and amount of information of the largest companies, with the ability to bring together several industries or even several business units.
Depending on the installation and where we use it
As it is a software, the place where we install it, use it and store the information, will always mark a type of ERP or another.
- On-premise ERP
By having the ERP system installed on our computers, we will always have more control over the data, security and, on the other hand, the updating of the system, although to obtain optimum performance, specialized training of personnel and hours of learning will be necessary.
Normally, linking this categorization with the previous one, larger companies are those that tend to have the staff and resources necessary to implement an ERP system on premise or on-premise. Confidentiality and not wanting third parties to store sensitive information about your organization also comes into play.
- Cloud ERP
This type of ERP system requires no installation, is accessed via the internet, is in the cloud and, usually, after a small step of creating an account, can already be used. Therefore, it has all the conveniences that an online service can give
us.
To comment, with respect to the ERP system in local, the user does not have the same level of control, but it is rewarded in the savings of time and business resources because they do not have to worry about issues such as maintenance, security or keeping the program updated manually.
10 recommendations to create a customized ERP for our business
When implementing our ERP there are a number of essential aspects to be clear about so that our system optimizes and helps to organize all the information of our organization in an efficient and effective way.

- Establish key objectives
Although ERP systems solve many problems of very different natures in organizations, it is very important to identify the real objective for which an ERP system is implemented, and KPI’s or performance indicators can help us to analyze and understand the need for ERP system intervention.
- Defining the scope
An equally important aspect as setting clear objectives is the definition of the scope, always taking into account the needs and opportunities of the company. A lack of definition at this point can lead to slower than expected ERP implementations or unplanned budget increases.
- Evaluate the possibilities
To carry out a successful or at least cost-effective implementation of an ERP system, the organization must make an effort to evaluate the options, paths and possibilities of the tool.
Management, together with the other departments involved, must be clear about the difference between ERP configuration and subsequent ERP customization to help the tool fit seamlessly with the organization and its information processes.
- Migrate data
To ensure that the system is not overloaded, it is important that only the necessary and most important data is transferred to the system. In addition, in order to be able to retrieve it when necessary, the organization should ensure that data and all relevant information is backed up periodically from time to time.
- Verify the infrastructure
This is one of the most important points in the implementation of an ERP system. Following the different categorizations mentioned above, the company has to fix together with its ERP system provider an infrastructure that fits the characteristics of its organization, always taking into account scalability.
- Customization
It may be that, depending on the company, an exhaustive customization of the system is not necessary. However, being a major investment decision of the company, it is recommended to allocate resources and time to try to make the ERP tool as customized and adjusted to the specific needs of the company as much as possible.
- Managing change
An ERP system implementation can affect the routine of a company’s employees. That is why it is recommended that the management of an organization involves its employees and prepares them through courses and training so that they understand the importance of an ERP, how it can save them time and how it will increase their productivity.
- Knowledge transfer
One of the main aspects that come from the nature of the tool is to prepare and train employees to use it properly. Knowledge transfer ensures that the implementation of the tool is a success. The organization must ensure that suppliers understand its needs and prepare its IT department with technological knowledge.
- Manage pilot projects and testing
Testing is part of the process. The more flexible, the more open and the more we learn from mistakes that may be made at the beginning, the more knowledge about the tool and about our own information flows we will have. Rigidity can be counterproductive in an implementation as relevant and with cross-cutting implications throughout the organization as an ERP system.
- Touch up and maintain continuous support
Once tested in pilot projects, it is time to get started. Some companies take the opportunity to test again, in order to get more feedback and optimize its development.
Something to keep in mind is that an ERP system is not a one-time event, it is a tool that will be with us for a long time and therefore becomes a continuous process within our organization.
All these recommendations, or steps to follow, are essential for an optimal ERP implementation, something that will undoubtedly have an impact on the proper management of our business processes. An essential tool for our business, whether large or small, that will help us to automate processes, optimize administration and improve relevant organizational decision making.

